The U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) puts out many resources for learning about healthy eating for kids, but in 2020 they released new 2020-2015 dietary guidelines for all Americans. Within the 164-page document, there are four key recommendations to follow that all apply to children. Let’s talk about each one.

Guideline 1: Follow a healthy dietary pattern
This guideline states:
“Healthy eating starts at birth with the exclusive consumption of human milk, if possible, for about the first 6 months. If human milk is unavailable, infants should be fed an iron-fortified commercial infant formula (i.e., labeled “with iron”) regulated by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), which are based on standards that ensure nutrient content and safety. Healthy eating continues with the introduction of complementary foods and beverages at about 6 months of age. By 12 months, infants should maintain their healthy eating as they transition to developmentally appropriate foods and beverages. Healthy eating continues in each life stage thereafter.”
The guidelines also recommend a vitamin D supplement 400 IU per day for breastfed infants. You might be wondering, once you start to introduce solids, what should you feed your kids?
“At about 6 months, introduce infants to nutrient-dense complementary foods. Introduce infants to potentially allergenic foods along with other complementary foods. Encourage infants and toddlers to consume a variety of foods from all food groups. Include foods rich in iron and zinc, particularly for infants fed human milk.”
The authors also note to avoid added sugars, foods high in sodium, honey, and unpasteurized foods when starting out with solids. For toddlers, they suggest roasted vegetables instead of fried ones, cereals with minimal added sugars, vegetables instead of high-sodium snacks, and unsweetened beverages.
As children grow, the USDA recommends this for daily intake:
- Ages 2-4: 1,000-1,600 calories
- Ages 5-8: 1,200-2,000 calories
- Ages 9-13: 1,400-2,600 calories
- Ages 14-18: 1,800-3,200 calories
Variety and balance are important, and the U.S. government recommends using its MyPlate guidance to achieve this.
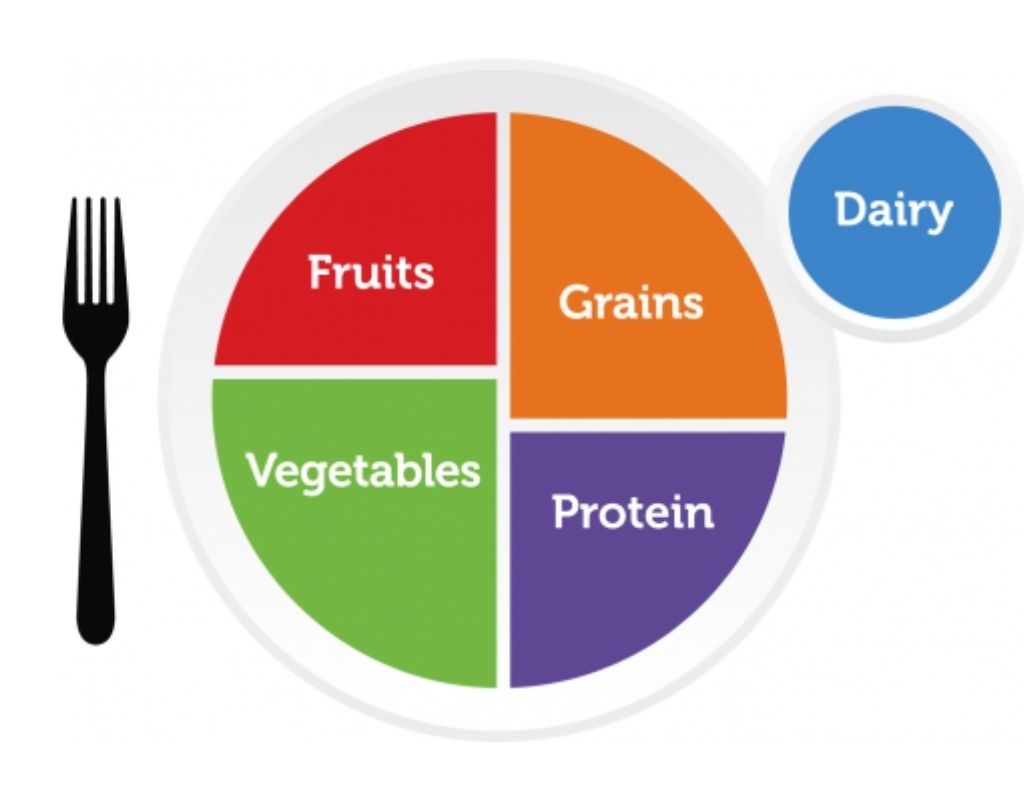
Guideline 2: Customize and enjoy nutrient-dense choices
Eating should be enjoyed, so feed kids foods they like. There’s an incredible diversity within food groups, so if you’re trying to feed your child spinach and they just won’t have it, try a different green vegetable like broccoli, bok choy, edamame, green beans, cucumber, or asparagus. You can blend these into other meals (like peas in mac and cheese) or cut them into fun shapes to make them more appealing. Take into consideration personal preferences, cultural traditions, and budgetary considerations when designing these customized choices.
Guideline 3: Focus on meeting food-group needs while staying within calorie limits
The guidelines recommend feeding kids “nutrient-dense” foods, which means that you get more nutrients in a smaller amount. The guidelines define nutrient-dense foods and beverages as ones that “provide vitamins, minerals, and other health-promoting components and have little added sugars, saturated fat, and sodium.” As you might have guessed, these are foods like vegetables, fruits, whole grains, seafood, eggs, beans, lean meats, and fat-free and low-fat dairy products. The guidelines also note that vegetarian children can meet protein needs through plant-based protein.
Guideline 4: Limit foods and beverages higher in added sugars, saturated fat, and sodium
The document suggests using the “85-15 guide,” which lays out that “85% of calories are needed per day to meet food group recommendations healthfully, in nutrient-dense forms” and that “15% of remaining calories are available for other uses (including added sugars and saturated fat).” That means chips, candy, and Popsicles should make up no more than 15% of what your child consumes in a day.
The two most common high-sugar foods Americans consume are sugar-sweetened drinks (sodas and fruit juices) and sweet snacks and desserts (cookies, ice cream, cake, etc.), so start your child off with healthy habits by limiting how often these are offered. The guidelines also note that the most common sources of saturated fats are sandwiches and desserts.
While reading 164 pages seems daunting, it’s worth glancing through the USDA guidelines document yourself. It lays out answers to every question like how many grams of each vitamin and mineral should be consumed per day, recognizing hunger signs, suggested meals, lists of healthy foods, and more. The website DietaryGuidelines.gov also has infographics that are easier to browse and a summary of the top 10 things you need to know. Remember to keep a balance of different food groups in mind and to limit sugary snacks, and you’ll be well on your way to building healthy eating habits for your child in line with the USDA guidelines for kids.




