As a parent, you and your children will experience plenty of rites of passage. Some are exciting (first steps and riding a bike). Others, not so much. It’s safe to say a run-in with head lice falls into the latter category. It’s a situation every parent dreads, but most experience it at least once in their life. Head lice is a common and harmless issue, but you’d probably prefer your child to bring home slime and glitter than this pesky problem.
You may wonder: What does head lice look like? Is there anything to do to prevent it? Can I make it go away sooner rather than later? Should I send my child to school?
We’re here to end your trip down the head lice rabbit hole. Here’s a heads-up on all things head lice.
Everything you – unfortunately – need to know about head lice
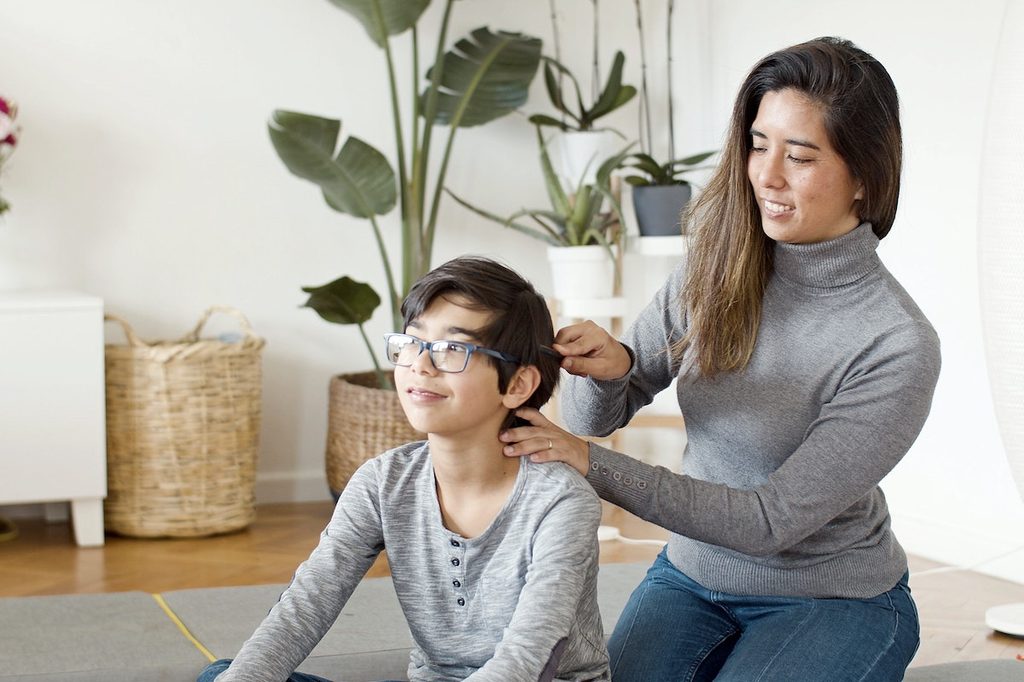

Understanding what to look for and how to react allows you to help your child treat and prevent head lice.
What does head lice look like?
Head lice are tiny, light gray bugs. One louse (the singular form of lice) typically measures about 2 to 3 millimeters — the size of a sesame seed. Though very small in size, head lice can quickly become a massive inconvenience. Head lice need to consume human blood to live, so these tiny bugs set up shop on a person’s scalp, usually a child.
If that weren’t enough, head lice also lay and attach their eggs at the base of the hair shaft near the person’s scalp. These white, oval-shaped eggs start at about 0.8 millimeters and are called nits. A female louse can lay 10 eggs per day. They hatch after about a week and grow up quickly, becoming adult lice by 12 to 14 days.
How does head lice spread?
Head lice is very common. According to the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP), millions of preschool and school-aged children develop head lice yearly. Head lice don’t fly like other insects, such as bees, though. Instead, they spread via prolonged head-to-head contact. Young children may butt or touch heads as part of play, making them more susceptible to head lice.
Rarely, but sometimes, head lice can spread through sharing items like hairbrushes, helmets, and baseball caps.
Signs of head lice
Though head lice are common; these bugs can be a challenge to spot. You may not even realize a child has head lice for four to six weeks. Some common symptoms of head lice include:
- Increased scratching in the infected area
- Feeling like something is tickling the scalp by moving
- Difficulty sleeping (head lice can be more active in the dark)
- Head sores from scratching so often — open sores can become infected if left untreated
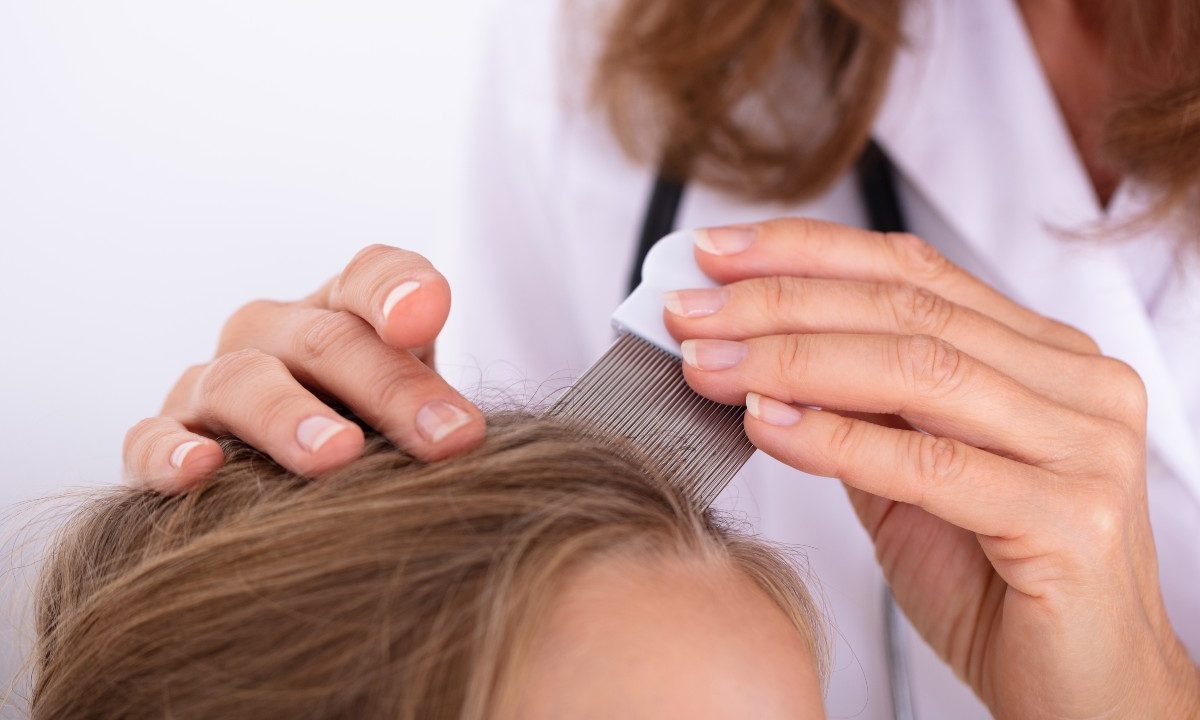
Head lice treatment
A doctor can diagnose your child with head lice. If diagnosed, treatment usually involves a “comb-out method” and medication. You should only use medication after consulting with your child’s pediatrician.
The comb-out method step-by-step is:
- Get your child’s hair wet.
- Comb through your child’s hair in tiny sections using a special fine-tooth nit/lice comb.
- Each time you comb through your child’s hair, use a paper towel to wipe the comb. Assess your child’s scalp, comb, and paper towel.
- Keep going until you have combed the entire head of hair.
It can take two to three weeks for head lice to clear up.
How can I prevent head lice?
Head lice happen — kids are kids. However, you can encourage some behaviors to reduce your child’s risk of developing this issue, including:
- Discouraging head-to-head contact. Remember, lice don’t hop from head to head. Instead, it’s typically the result of prolonged hair-to-hair contact. Teach your child to play in other ways.
- Avoid sharing items that touch the hair. Though it’s rare for lice to spread via shared objects, it does happen. Encouraging your child to use their own comb and hat, and in this case, not sharing these items, can reduce head lice risk.
Guidelines for school attendance if a child has head lice
In 2022, the AAP updated its guidelines to emphasize that children don’t need to miss school because of head lice.
“The AAP states that head lice screening programs in schools have not been proven to have a significant effect over time on the incidence of head lice in the school setting, are not cost-effective, and may stigmatize children suspected of having head lice,” the statement read in part.
Is head lice dangerous?

Despite being a common issue among young children, and being a massive annoyance for parents, head lice is thankfully not dangerous. Although lice feed on blood from the scalp, they don’t transmit disease or bacteria, making them relatively harmless. However, although they may not be dangerous, they are easily transmitted making it important to treat them as soon as you become aware.
If lice go untreated for an extended period a person may develop anemia, according to Lice Clinics of America. Lice bites can also cause rashes, so it’s important to treat the affected areas as soon as you notice a problem.
An important note on head lice
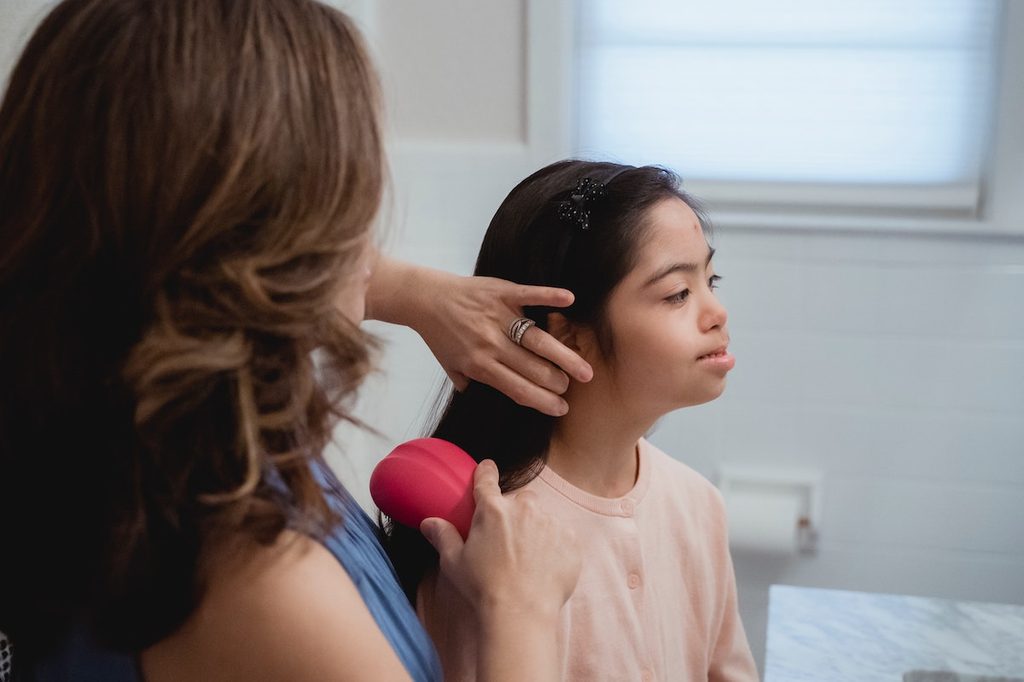

Head lice can be a source of embarrassment. It’s essential to remember that head lice isn’t the result of poor hygiene. Other kids should not make fun of, bully, or socially ostracize children for having head lice — be kind.
Closing thoughts on head lice

Though head lice is an annoying issue to deal with, it is harmless. Your child isn’t in danger, and they don’t have to miss school. Scratching and feeling like something is “tickling the head” are common signs of head lice. Those symptoms can take a while — sometimes six weeks — to develop. One risk of lice: Sores from scratching can become infected if not treated, so keep an eye on them if your child develops them.
Discourage play that involves hair-to-hair contact, and keep sharing of combs/brushes and caps to a minimum, if at all. These steps can help reduce the likelihood that your child will develop head lice. If you suspect head lice, speak with your child’s doctor. They can help nix the issue.